JULY 2025
Publications & Media Mentions
Risk-Based Breast Cancer Screening: Insights from the EUCanScreen Delphi and Systematic Review
WP9.5 has achieved its goals and is preparing 2 publications and has submitted 3 conference abstracts on the matter.
Risk-based breast cancer screening (RBBCS) is an emerging approach aimed at tailoring screening strategies to individual risk profiles. As part of the EUCanScreen initiative a Delphi process was conducted to assess expert consensus on the current state of evidence and implementation needs for RBBCS.
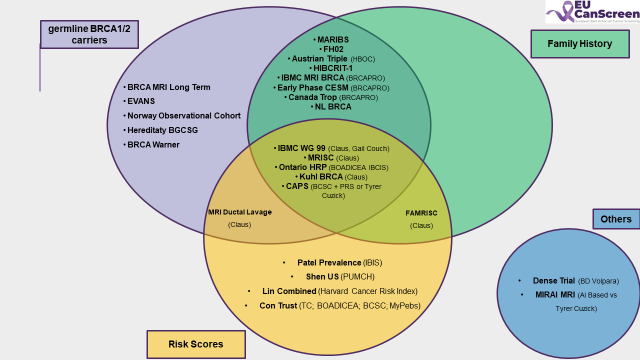
We conducted a systematic review of completed and ongoing (ong) studies on RBS worldwide. Eligible studies were identified through PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov and a structured survey within the EUCanScreen network. Data were reviewed by 3 independent investigators (PROSPERO 616967).
A two-round Delphi survey was carried out between May and June 2025 among European experts in risk-stratified screening. Fourteen evidence-based statements covering effectiveness, acceptability, harms, feasibility, and implementation challenges were evaluated. Consensus was defined as ≥85% agreement.
Conclusions
While cohort studies have demonstrated the impact of screening escalation among BRCA1/2 carriers, other RBS studies have not yet reached a sufficient level of evidence (LoE) to change practices. Major escalation and de-escalation studies in the general population are awaited in the upcoming years.
The Delphi process identified strong expert consensus on key aspects of RBBCS, while highlighting persistent evidence gaps in implementation, acceptability and risk threshold definition. These findings emphasize the need for real-world data and support the development of evidence-informed risk-based screening strategies across Europe.
Authors
Maria Agustina Ipina, Suzette Delaloge, Gustave Roussy
Paola Mantellini ISPRO
Subscribe to our newsletter to get news and updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get news and updates.

The general objective of EUCanScreen is to assure sustainable implementation of high-quality screening for breast, cervical and colorectal cancers, as well as implementation of the recently recommended screening programs – for lung, prostate and gastric cancers. EUCanScreen will facilitate the reduction of cancer burden and achieving equity across the EU.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s EU4HEALTH Programme under the Grant Agreement no 101162959